Urology
Renal Cancer Treatment
UrologyRenal Cancer
With the increasing popularity of health checks and body imaging, many cases of renal cancer can be detected at an early stage, where surgical resection has a cure rate exceeding 90%.
Surgical options include total nephrectomy or partial nephrectomy. Total nephrectomy involves the complete removal of the entire kidney along with the tumor, while partial nephrectomy involves removing only the tumor while preserving the remaining normal kidney tissue. Studies have found that if the renal tumor is 5 cm or smaller, total nephrectomy and partial nephrectomy have similar cure rates. Furthermore, partial nephrectomy allows for the preservation of more normal kidney tissue, reducing the chances of future chronic kidney failure and the need for dialysis, improving the long-term survival rates for patients.
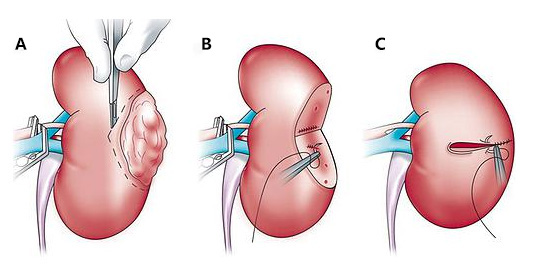
(Principles of partial nephrectomy)
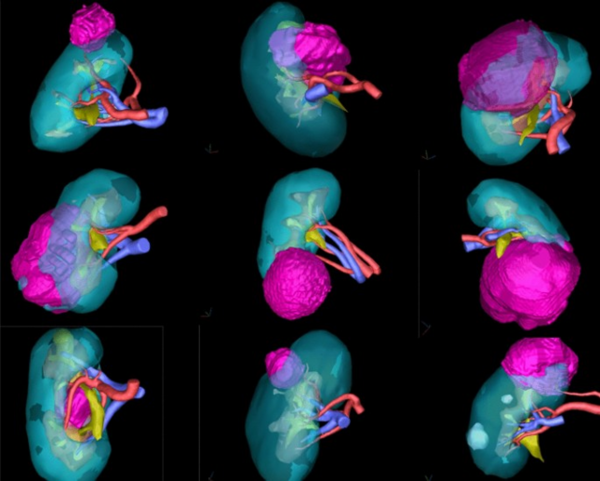
CUHK Medical Centre has acquired the latest software for 3D imaging reconstruction for partial nephrectomy. It enables precise analysis of renal vascular anatomy, tumor location and surrounding structures for improved surgical outcomes.
Renal Cancer Treatment Options
Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery
Robotic assisted laparoscopic surgery
Open radical nephrectomy
Percutaneous tumor ablation
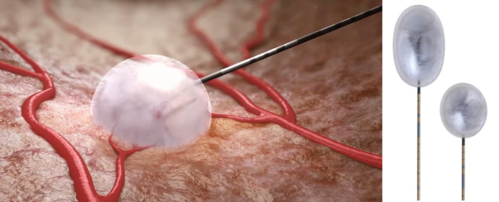
Cryoablation
Cryoablation utilises argon-helium gas and the Joule Thomson effect to produce freezing and thawing effects within the tumor, hence killing tumor cells.
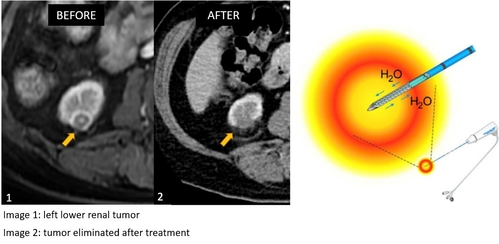
Radiofrequency ablation
In radiofrequency ablation, the fine needle put into tumor releases radiofrequency energy and generates heat energy within the planned treatment area, raising the temperature to over 60 degrees Celsius to achieve the effect of killing tumor cells.
Late Stage or Metastatic Renal Cancer
Postop recurrence rate for renal cell carcinoma with lymph node metastasis or high grade cancer is still relatively high. Apart from regular imaging surveillance, these types of high-risk patients can now undergo adjuvant immunotherapy to reduce the chance of recurrence.
As for late stage or metastatic renal cancer, conventional chemotherapy or target therapy are not sufficient for disease control. In recent years, newer combination therapy with PD-L1 inhibitors are bringing new hopes to suitable patients for improved survival outcomes.












