Hernia
Hiatal Hernia
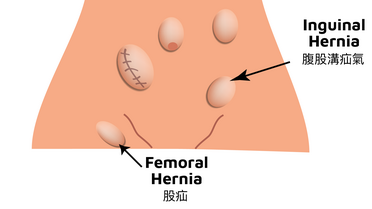
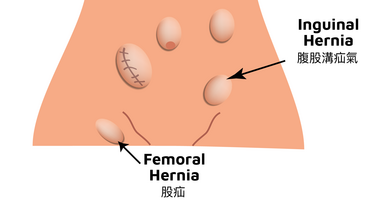
HerniaHernias

Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia is different from other abdominal hernias in that the abdominal contents protrude into the chest rather than outside the skin. The diaphragm is a muscle that helps us breath and separates the chest from the abdomen. In some patients, the opening allowing the passage of the oesophagus and stomach becomes loose, resulting in a portion of the stomach protruding into the chest. Occasionally if the opening is large, then other organs such as the spleen, colon, pancreas, or small intestine can also protrude into the chest. Increasing age, obesity, and smoking are known risk factors in adults.
Hiatal hernias are very common, especially in people over 50 years old. Symptoms may include acid reflux, chest pain, heartburn, or difficulty in swallowing.
Treatment
The aim treatment are to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. Your reflux can usually be treated with medications that neutralize stomach acid. Surgery can be considered if you do not want to be on long-term medications or if the medications fail to control your symptoms or if complications such as obstruction or anaemia occurs. Typically, this type of hernia is repaired using laparoscopic or robotic techniques.