Varicose Veins Clinic
1/F, CUHKMC
Introduction
The Varicose Veins Clinic provides assessment and personalised treatment for patients with varicose veins. Under the guidance of specialists in General Surgery, the clinic's objective is to offer professional assessment, diagnosis, and surgical treatment for patients. The clinic is located in the Specialist Outpatient Centre at CUHKMC and provides a professional and comfortable environment for consultation.
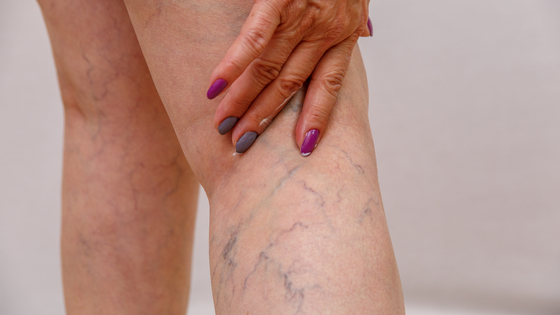
What is varicose veins?
Varicose veins are twisted, enlarged veins. Any vein that is close to the skin's surface (superficial) in the legs can become varicosed. Varicose veins only affect the veins in the legs because standing increase the pressure in the veins of the lower body.
Our Services
Diagnosis of Varicose Veins
In addition to a thorough patient history and physical examination conducted by a specialist, a Duplex Ultrasound Vein Scan can accurately assess the anatomy and functionality of your veins, helping determine the most suitable treatment approach.
Diagnostic test by Duplex Ultrasound Vein Scan
- Evaluate the veins in the lower limbs, specifically for varicose veins
- This bedside investigation is painless
Surgical procedures
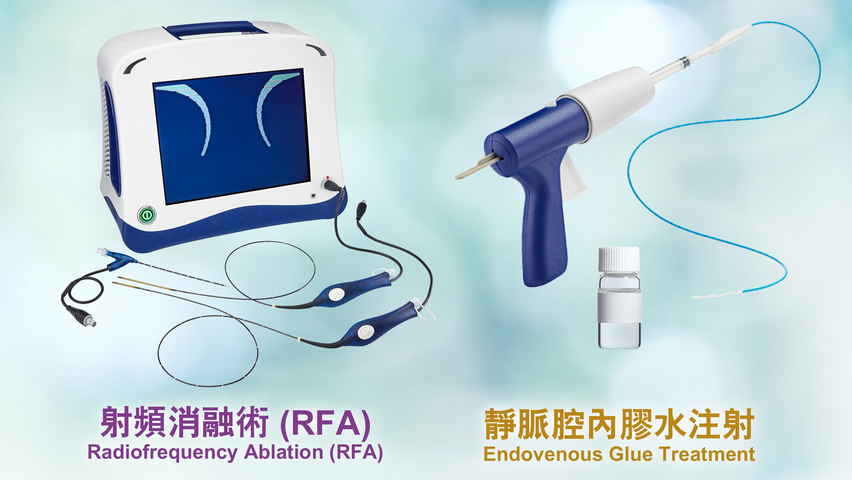
Varicose Vein Surgery
- Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT)
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- Endovenous Glue Treatment
- Hook Phlebectomy
- Foam Sclerotherapy
Health Knowledge on Varicose Veins
Common symptoms of varicose veins
- Visible, twisted, or bulging veins that appear dark blue or purple
- Achy or heavy feeling in the legs
- Swelling, especially after prolonged sitting or standing
- Itching or irritated skin around the affected veins
- Muscle cramps or aching in the legs, particularly at night
What are the causes of varicose veins?
Varicose veins develop as a result of weakened walls in the superficial veins, leading to stretching. This stretching causes the failure of one-way valves within the veins. Normally, these valves only permit blood to flow upward towards the heart. However, when the valves leak, blood can flow in the wrong direction when standing, resulting in reverse flow known as venous reflux. This increased pressure on the veins causes them to bulge and become varicose.
Varicose veins can also be caused by occupations that involve prolonged standing or weight-bearing, which increase pressure on the leg veins. They often appear during pregnancy and while they may become less prominent in the weeks following delivery, they typically do not disappear completely. Additionally, varicose veins often have a genetic component (the exact inheritance pattern is not well understood) and are more likely to occur as one gets older.
What issues can varicose veins cause?
The elevated pressure inside the veins can result in various symptoms such as aching, throbbing, itching, swelling of the ankles, and leg cramps. As normal blood circulation is disrupted, if left untreated, complications such as eczema, brown discoloration, ulceration, clot formation, bleeding, infection, and even skin cancer may arise.
Factors contribute to the development of varicose veins
- Age: The risk of varicose veins increases with age as the veins lose their elasticity and become weaker
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop varicose veins, mainly due to hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause
- Family history: If your parents or close relatives have varicose veins, you have a higher risk of developing them
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy increases the volume of blood in the body, and hormonal changes can weaken vein walls, making varicose veins more likely to develop
- Prolonged standing or sitting: Jobs that require long periods of standing or sitting can increase the risk of varicose veins
Prevention of Varicose Veins
Patients can alleviate discomfort associated with varicose veins and prevent their progression, as well as the development of spider veins and reticular veins, by following these measures:
- Maintain weight control
- Engage in regular exercise to enhance muscle strength and promote venous blood flow
- Elevate the legs and engage in frequent leg movement to improve venous blood circulation
- Lie flat while resting to prevent venous stasis
- Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing
- Perform leg exercises every 30 minutes during prolonged sitting
- Shift body weight every few minutes during extended periods of standing
- Avoid wearing high heels for extended durations
- Use leg compression stockings
- Refrain from wearing tight clothing that restricts the trunk, hip, and thigh
Frequently Asked Questions
Following minimally invasive varicose vein surgery, there is no requirement for bed rest or hospitalisation. You are free to resume your normal activities on the same day. Dressing will be preformed on the 2nd day of surgery , off stitch on 7th day. Patient should wear long compression socks for 2 days and follow with short compression socks for few weeks.
Varicose veins can be influenced by various factors, including age, gender, family history, number of pregnancies, obesity, and occupation. Here are some key considerations:
- Age: Varicose veins are typically more prevalent in individuals aged 40 and above
- Gender: Females have a higher tendency to develop varicose veins compared to males
- Family history: If a family member has experienced varicose veins, there is a relatively greater risk for other family members
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the likelihood of developing varicose veins
- Pregnancy: Around 40% of pregnant women have a chance of developing varicose veins, with a higher relative risk for women who have had multiple pregnancies
- Occupation: Occupations that entail prolonged periods of standing, such as cooks, barbers, nurses, and shop floor salespersons, can contribute to the development of varicose veins
The most effective method of prevention is leg elevation, regular lower body exercises, such as running, which helps the muscles in the feet generate enough pressure during exercise to promote blood circulation towards the heart. If you have to stand for extended periods at work, wearing compression socks can prevent blood pooling in the lower limbs by applying external pressure. Compression socks are specifically designed for this purpose, and they should be at least grade 2 (with a pressure of 20-30 mmHg) or higher to provide adequate pressure for improving venous reflux. Additionally, medications such as micronised flabonoid could increase tension of blood vessel and serve as an option for symptom management.
In the initial stages following the operation, varicose blood vessels may still be present in the calf. To assess the success of the surgery, the patient can lie on a bed and elevate their legs above heart level, allowing the blood to flow back towards the heart. Then, by promptly lowering the legs, the patient will observe the previously bulging blood vessels becoming sunken. This indicates a successful surgery, as it signifies that the damaged saphenous vein, affected by the faulty valve, has been effectively treated.
When it comes to recovery time and recurrence rate, minimally invasive varicose vein surgery is superior to traditional open surgery. In foreign countries, minimally invasive varicose vein surgery is considered the "gold standard" for treating varicose veins and lower the recurrent rate.
There is a common misconception among patients that varicose veins are solely a matter of appearance, resembling thick, worm-like blood vessels. However, it is important to note that severe varicose veins can lead to complications such as leg ulcers, bleeding, and even an increased risk of developing skin cancer over time
Download
Health Knowledge
View AllMedical Team
View AllCUHKMC Medical Team

















 Booking: (852) 3946 6888
Booking: (852) 3946 6888 1/F, CUHKMC
1/F, CUHKMC